APARC Visiting Scholar Sheds Light on the Cold War Roots of Contemporary Urban Politics in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia’s megacities, long viewed as symbols of progress, are facing crises ranging from floods and ecological damage to displacement and widening inequality. Scholars of contemporary urban politics often attribute these predicaments to rapid globalization that originated in the mid-1980s. Yet APARC Visiting Scholar Gavin Shatkin argues they must be understood in the context of the Cold War era, when urban development agendas were molded by authoritarian regimes exerting political and economic control in the name of anti-communism.
Shatkin, an urban planner specializing in the political economy of urbanization and urban policy and planning in Southeast Asia, is a professor of public policy and architecture at Northeastern University. He recently completed his residency at APARC as a Lee Kong Chian National University of Singapore-Stanford fellow on Southeast Asia. Before heading to Singapore for the second part of his fellowship, he presented research from his new book project, which examines how U.S.-supported authoritarian regimes in Indonesia, the Philippines, and Thailand shaped urban politics in three megalopolises —Jakarta, Bangkok, and Metro Manila — during the 1960s and 1970s, with consequences that reverberate today.
Political Violence as Foundation
Shatkin refers to the period from the mid-1960s to the mid-1970s as Southeast Asia's "hot Cold War." During that time, in tandem with the armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia, political violence spread through Indonesia, the Philippines, and Thailand, as the three countries witnessed the emergence of authoritarian regimes that cemented their rule by manipulating laws and institutions and deploying targeted, often extreme violence justified as necessary to combat communism.
In Indonesia, a U.S.-backed 1965 military coup, directed particularly at the Communist Party of Indonesia, led to the massacre of 500,000 to one million people, heralding General Suharto's 32-year authoritarian rule.
In the Philippines, amid leftist demonstrations and a communist insurgency, President Ferdinand Marcos declared martial law in 1972, marking the beginning of a decade defined by his administration’s widespread human rights violations, throughout which the United States continued to provide foreign aid to the country, considering Marcos a steadfast anti-communist ally.
And in Thailand, the imposition of the 1958 military dictatorship to counter communist threats and the 1976 crackdown by Thai police and right-wing paramilitaries against leftist protesters were pivotal points in establishing a royalist-nationalist model that defined "Thainess" (khwam pen thai) through loyalty to the monarchy, aligned with military power as well as American military aid and counter-insurgency policy guidance.
According to Shatkin, these were not isolated incidents but defining episodes of political violence that cemented authoritative oligarchic control over urban development. The explosive urbanization in Southeast Asian cities that followed in the mid-1980s must be read through the lens of this earlier period, when authoritarian regimes sought to exploit urban transformation to entrench political and economic power.
Oligarchic Politics
The Suharto regime's approach to Jakarta as a source of profit exemplifies this dynamic. Shatkin explains how, between 1985 and 1998, Indonesia's National Land Agency distributed land permits for extensive urban development across the Jakarta metropolitan region to a small network of oligarchic conglomerates, such as the Salim Group. These crony corporations, allied with Suharto through family ties and political patronage, came to dominate Indonesia’s economy. Many of these same corporate interests continue to influence development agendas in Jakarta today, owning exclusive rights to purchase and develop permitted land.
The same pattern of successive waves of government expansion of metropolitan regions through infrastructure development and the distribution of land to selected major conglomerates has repeated itself in Manila and Bangkok, creating in-country profit centers for economic interests and what Shatkin calls “an archipelago of exclusive gated elite spaces” that reinforces spatial dichotomy and segregation as each of these megacities also experiences a housing crisis.
For example, Shatkin’s research in Metro Manila during the late 1990s and early 2000s revealed that approximately 40% of the population lived in dense informal settlements. A significant portion of these residents were employed in the nearby container port, yet their wages were insufficient to afford legal housing near their workplace. This discrepancy highlights a structural dilemma where low-wage workers are effectively compelled to occupy land illegally.
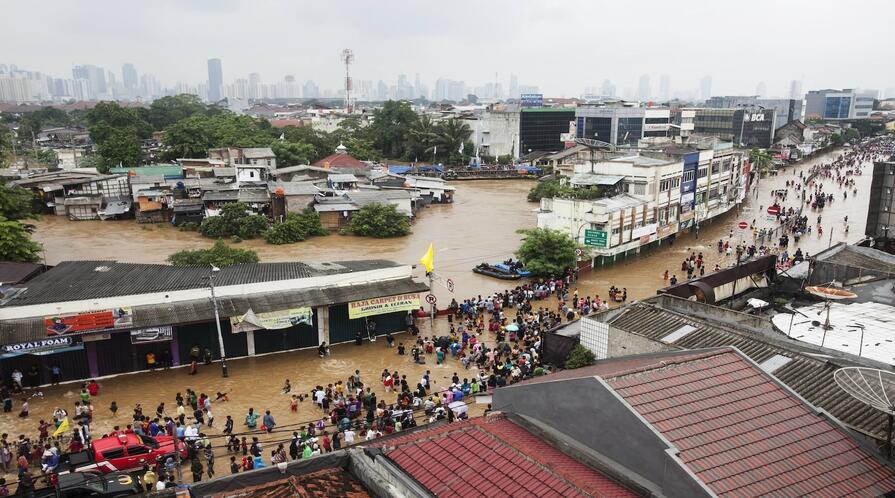
Environmental crises in the three urban giants are also entrenched in political and social structures rooted in oligarchic and authoritarian legacies of the Cold War era, argues Shatkin. Thus, increasingly devastating floods in Jakarta, Metro Manila, and Bangkok have less to do with sea level rise and far more with the rapid spread of impervious surfaces and the extraction of groundwater resulting from uncontrolled urban sprawl on converted watershed lands within a relatively weak regulatory environment. Moreover, flooding mitigation solutions, like Indonesia’s Great Garuda seawall project, have perpetuated the same pattern of land giveaways to major developers.
Lessons from Urban Social Movements
Crucially, Shatkin's research shows that Southeast Asian urban activists themselves frame their struggles through the lens of Cold War legacies. For example, when Jakarta residents along the Ciliwung River faced eviction for flood mitigation in 2015, they challenged the Jakarta administration and the Ciliwung-Cisadane Flood Control Office in court, arguing the eviction was based on a Cold War-era law drafted during counterinsurgency operations that had no place in democratic Indonesia. They partially won the case.
In a similar vein, Thailand's Red Shirt movement, representing working-class people from the northeast, deliberately protested on land owned by the Crown Property Bureau, using iconography that critiqued the military-monarchy-elite alliance forged during the Cold War.
An example from Manila is the 2001 mass protests by urban, low-income groups in defense of President Joseph Estrada, who was impeached for corruption. Their support can be interpreted as a reaction against “anti-poor” discourse that originated in the Ferdinand Marcos era. For the urban poor, Estrada represented a powerful counterweight to this legacy of elite disdain.
"We need to listen to these protest movements on the ground,” says Shatkin. They do not primarily critique globalization but rather contest entrenched oligarchy and state paternalism forged by Cold War political violence. Thus, an alternative framework for understanding debates in urban politics of Jakarta, Manila, and Bangkok is to view them not merely as capitals shaped by globalization but as Cold War frontline sites.
Beyond Southeast Asia
The implications of Shatkin’s theoretical framework extend beyond Jakarta, Metro Manila, and Bangkok, and even beyond Southeast Asia. It illuminates how periods of political upheaval create enduring social, economic, and environmental inequalities.
Moreover, these three urban giants, which produce outsized shares of their nations' GDP, rank among the world's largest cities. Their futures will not only affect Southeast Asia but also global urban development patterns. Shatkin's work suggests that this future cannot be charted without reckoning with the past.
Read More

Gavin Shatkin, a Lee Kong Chian NUS-Stanford fellow on Southeast Asia at APARC, argues that prevailing urban development challenges in Jakarta, Metro Manila, and Bangkok stem from Cold War-era political and institutional structures imposed by U.S.-backed authoritarian, anti-communist regimes.