The Future of U.S.-China Relations: A Guardedly Optimistic View
David Meale, former U.S. diplomat and current consultant, offered a cautiously optimistic perspective on U.S.-China relations at an APARC China Program seminar, arguing that despite significant tensions, there remains substantial room for what he calls “managed rivalry”—a relationship that is neither warm nor easy, but constructive enough for both countries to serve their populations and address global challenges. Drawing on his 33 years in the U.S. Foreign Service, he traced the evolution of U.S.-China relations over the past three decades and assessed current trajectories, bringing both diplomatic experience and fresh insights from private sector concerns to his analysis.
Three Decades of Evolving Relations
His entry into China-focused diplomacy came in 1995 when he was assigned to Hong Kong during the handover. During that era and through the early 2000s, U.S. policy operated under the assumption that China would gradually embrace the post-war rules-based international order shaped largely by the United States. The thinking was that China would develop a self-interest in preserving this order, becoming a constructive, if not easy, partner. This belief undergirded the strong U.S. effort to bring China into the World Trade Organization in 2001.
During his service as an Economic Officer in Taiwan in the 2000s, Meale witnessed the merging of talent from Asia and the United States that built China’s electronics manufacturing industry. Five percent of Taiwan’s workforce had moved to the mainland; there were even Shanghainese dialect programs on Taiwanese television at night for those dreaming of seeking their fortunes through cross-strait opportunities. Although there was tension with the Chen Shui-bian administration, there was a surprising amount of positivity in Taiwan about the mainland. That, of course, has now changed.
The Obama administration continued to work within the framework of bringing China into the existing international order, even as concerns grew. The approach aimed to convince China to preserve and, if necessary, shape this order, while using it to constrain China when necessary, as demonstrated by the attempt to resolve the South China Sea dispute involving the Philippines through the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
The Trump administration marked a decisive shift. Meale noted that Trump openly discarded the goal of integrating China into the existing order, instead pursuing aggressive trade policies, technology restrictions, and explicit framing of China as a threat. The Chinese hoped the Biden administration would turn this around, but it instead maintained this posture, pursuing an “invest, align, compete” strategy—investing in the United States, aligning with allies, and defining the relationship as a competition.
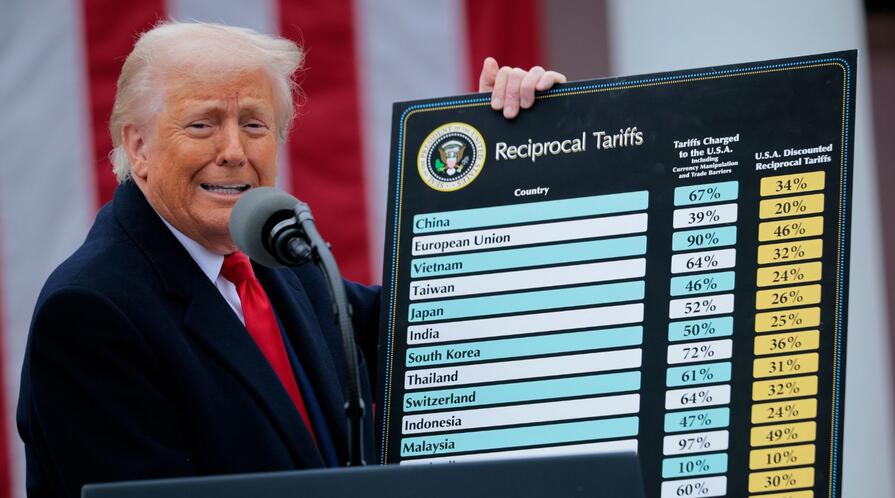
Trump 2.0 brought “Liberation Day,” which Meale sees as the belief that the U.S. place in the world needs to be corrected; the United States is economically overextended, the trade imbalances and the associated debt cannot continue, and the supply chain vulnerability from COVID must be addressed. Tariffs were ratcheted up, and both sides imposed export controls.
The Chinese hit back hard; Chinese officials are very proud of China’s pushback against an unchecked Trump. China’s economic growth is forecast at 5 percent this year, and the feeling from China is that it has shown the world the United States cannot push it around.
Looking ahead to 2026, Meale is optimistic. There will undoubtedly be crises that pop up: the Chinese will overreach on rare earth elements, and the United States will take an economic action that the Chinese did not plan on. Meale sees this as the “sine curve” of the U.S.-China relationship. There’s a crisis, tensions rise, there’s a response, and things eventually cool down. The curve goes up and down, but very little gets resolved.
Sign up for APARC newsletters to receive our event invitations and guest speakers' insights >
China's Current Challenges
China, Meale noted, effectively contains two economies: one serving approximately 400 million people who are producing world-class products with perhaps the world's best industrial ecosystem and impressive infrastructure, and another economy serving the rest of China's population, which has improved significantly over recent decades but relies heavily on informal work and the gig economy.
China faces deep structural problems, including a property sector crisis that has destroyed significant household wealth, an economy structured excessively around investment rather than consumption, youth unemployment reflecting a mismatch between graduating students and available jobs, and "involution" (neijuan, 内卷)—a race to the bottom in sectors where government incentives have driven overcapacity. China's reliance on export-led growth comes at a time when its overcapacity is increasingly unwelcome not just in developed countries but across the global South.
These challenges, Meale argues, will not result in a financial crisis or recession, but rather chronic headaches that will affect its foreign relations. Growth will continue, albeit at a slower pace, and the country will have significant work ahead to address inequality and structural imbalances.
On the question of Taiwan, Meale pushed back against predictions of imminent Chinese military action, particularly speculation about 2027 as a critical year tied to the 100th anniversary of the People's Liberation Army. He argued that, right now, one of China’s top goals is to avoid being drawn into a Taiwan conflict. China has recently purged nine senior military officials and is dealing with serious problems in its military. Five years from now, however, the situation could look quite different.
Defining End States and Finding Common Ground
Meale concluded by outlining what he believes each side seeks as an end state, arguing that these visions, while different, are not irreconcilable. Rather than global domination, he argued China seeks a world that works for what it calls "grand rejuvenation." This means overcoming the century of humiliation, reunifying with Taiwan, and living safely and securely on its own terms. China wants recognition as a global power, dominance in its near seas, freedom from technology containment, elimination of shipping chokepoints, access to markets, and the ability to pursue relationships with ideologically aligned countries.
The United States, meanwhile, accepts that competition with China is permanent but seeks a predictable China. U.S. goals include protecting advanced technology where it has an advantage, avoiding supply chain vulnerabilities, shaping Beijing's choices without attempting to control them, maintaining the Taiwan status quo until it evolves in a mutually and naturally agreed way, and ensuring fair trade to address what it sees as a stacked deck in current trade relationships. The United States also wants to prevent China from enabling adversaries, as seen in Chinese firms rebuilding Russia's military-industrial complex while maintaining nominal neutrality on Ukraine.
These end states, Meale acknowledged, collide in many ways but not in absolute ways. He sees substantial room for leader-driven, managed rivalry that can function constructively. This rivalry will not be easy or warm, but it can allow both countries to serve their populations while cooperating where global interests align.
Key Takeaways
- The “integrated China” assumption is over. U.S. policy no longer aims to bring China into the existing international order, marking a fundamental shift from decades of engagement strategy.
- China's economy faces structural challenges, not a crisis. China will continue to grow, but must address inequality, overcapacity, and wealth destruction from the property crisis.
- Taiwan timing matters more to Beijing than deadlines. China seeks to control when and how the Taiwan issue is resolved, preferring not to be forced into premature action.
- Managed rivalry is possible. Despite significant tensions and incompatible elements of each side's goals, there remains space for constructive competition. While the relationship between the world's two largest economies will stay competitive and often contentious, it need not become catastrophic.
Read More
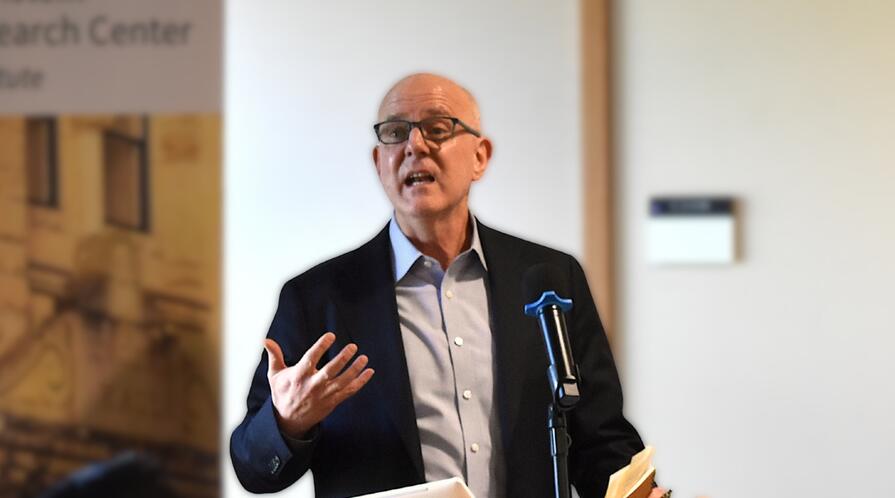

Eurasia Group’s David Meale, a former Deputy Chief of Mission at the U.S. Embassy in Beijing, reflects on the last 30 years and describes how the two economic superpowers can maintain an uneasy coexistence.