REAP co-director Scott Rozelle begins a ten-part series for Caixin Magazine titled, "Inequality 2030: Glimmering Hope in China in a Future Facing Extreme Despair." Rozelle explains why continued high income inequality could spell trouble for China's future growth and stability.
To read the column in Chinese, click here.
> To read Column 2: China's Inequality Starts During the First 1,000 Days, click here.
> To read Column 3: Behind Before They Start - The Preschool Years (Part 1), click here.
> To read Column 4: Behind Before They Start - The Preschool Years (Part 2), click here.
> To read Column 5: How to Cure China's Largest Epidemic, click here.
> To read Column 6: A Tale of Two Travesties, click here.
Inequality 2030:
Glimmering Hope in China in a Future Facing Extreme Despair
Column 1: Introduction and why we need to worry about inequality
Inequality is underrated
China’s growth slowed in 2012 and in the first half of 2013. And, the world is holding its collective breath. Can China’s once white-hot economy be re-ignited and continue to blaze ahead? Or has its economy finally begun its inevitable slow down, a braking that all countries that reach middle income levels of development experience.
While the financial pundits and economic crystal ball gazers are focused on growth rates and world economy spillovers, we are worrying about another indicator: China’s level of inequality. In fact, we believe that what happens to inequality in the future is probably more important in the long run than growth. Whether high or low, we believe the nation’s income distribution will be one of the most important determinants of the quality of life in China in the 2030s.
Why is inequality more important than growth? Of course, nominally both are important. China needs to maintain 6 to 8 percent over the next 10 years. China needs to continue to grow 4 to 6 percent until 2030. However, we believe that as China’s economy matures over the next two decades, growth will slow. The growth rates of healthy, developed economies are never more than 2 to 3 percent. This slowing is inevitable. It is a done deal. Inequality, on the other hand, could be high or low. And, if it is high: China could be in for a troubled adulthood. It could even be headed for stagnation. High inequality could even lead to collapse and the loss of all things good that have been built up over the past three decades.
Remedial learning about Inequality and the Middle Income Trap
So what allows some countries to successfully transition from middle to high income? Solid banking practices: important. Good corporate governance: a must. Competition policy: few would argue. In this part of the column we want to put forth an argument that an equitable income distribution is also a necessary ingredient for long-run, stable growth. The basis of this statement is an empirical regularity that characterizes nearly every case of successful development (during the shift from middle to high income) in the last half of the 20th century.
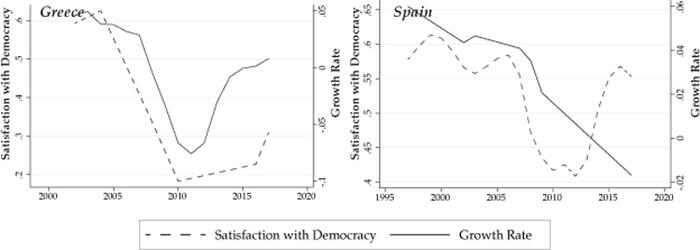
Since 1945, we can divide the world into three groups of countries. The high income countries, like the US, the UK, Germany and France; the poor and chronically underdeveloped; and the new members of the OECD club. Somewhat surprisingly, over the past 70 years, there have been only 15 or so countries that have graduated from poor to middle to high income. The list includes two East Asian countries/regions (South Korea and Taiwan); four Mediterranean countries (Portugal; Spain; Greece and Israel); six Eastern European countries (Croatia; Slovenia; Slovak Republic; Hungary; Czech Republic and Estonia; and two other countries (Ireland and New Zealand).
Most salient for our column is that in the case of all of these successful countries an equitable income distribution is feature they all share. This is true goingback as early in their development paths as possible. Using a popular measure of inequality, the Gini ratio (where 0 is perfect equality and 100 is perfect inequality), it can be shown that the average Gini ratio of the new members of the OECD club is only 33, a level of the Gini that is relative low. The range of the Gini measures for these successfully graduating countries is from 26 to 39. Not one of the Gini ratios is more than 40. Such a pattern of income distributions suggests that, on average, those countries that were successful in moving from low to middle to higher income not only share a common growth path, successfully took them from middle to high income, all of the nations did so with fairy low levels of inequality.
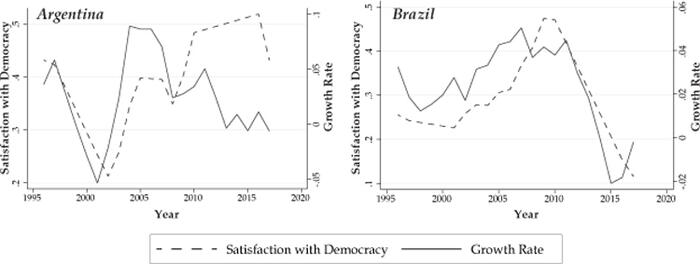
Such low levels of inequality for the successfully developed countries can be seen to be in stark contrast to the countries in the world that grew, hit middle income status and then ultimately stagnated or collapsed. Argentina, Brazil, Iraq and Mexico are examples of countries that had rapid spurts of growth, joined the ranks of the world’s middle income countries, only to find their growth aspirations squashed. These countries all were striving to become high income, industrialized, developed countries. At some point during the past 70 years, however, each of these countries experienced either dire collapse or long and frustrating stagnation.
What is a characteristic that all of these failed-to-move-up-from-middle-income countries share? When comparing the Gini ratios of these wannabe-but-never-made-it nations with those that successfully graduated, there could not be a greater contrast. Whereas there were no successful developed countries with a Gini ratio over 40, there were no countries that experience growth and stagnation/collapse with Gini ratios under 40. The Gini ratios of Brazil and Mexico and Iraq were all around 50.
So where is China on this list? China’s level of inequality, according to one of the most complete and internationally comparable study done at Beijing Normal University by Professor Li Shi and his colleagues, is among the highest in the world. As of 2007, it was 50 (or 49.7 to be precise). Between 2003 and 2007 it rose more than any country in the world. Others say it is higher—see the work of Li Gan from Sichuan University. Hence, although China has attained middle income status in the past decade, it also is part of a group of countries that is trying to transition to high income status at levels of inequality which have not ever been associated with successful transition—at least not in the past 70 years.
What is the problem with high inequality?
So why is it that inequality is so inimical for a middle income country striving to reach high income? We believe the reason is twofold. The first has to do with the inevitability of growth slow down and expectations. When a country is growing fast (as countries can do when they are moving from poor to middle income—as China has been over the past three decades), even if there is a high level inequality, most people in society have expectations that they will be better off if they stick inside the system. In China during the past several decades, even for those at the lower end of the income distribution, their standard of living is higher now than 10 years ago. Relying on extrapolations from the past, most people believe that they will continue to become better off. At the very least they will tell you that they expect their children will be able to live a better life in the future.
High growth has made these rising expectations possible—even for the poor. There has been enough for all to “go around.” Hence, with positive expectations about being able to get better in the future, even facing long working hours, cruel living conditions and low wages, individuals have chosen to work “inside the system.” For most, working in the system mean that they get a job, save as much as possible and look forward to making even more and having more savings in the future.
This whole system, however, is predicated on growth trickling down to the poor. If growth slows, it is possible that the expectations may not be realized. We believe that it is these expectations that have produced the glue holding society together—despite the high levels of inequality. The key question or the real fear is that when expectations are popped, individuals may decide to opt out of the system into the informal or even the gray/black economy.
The second problem with high income inequality is that it often is accompanied by high inequality in education, nutrition and health. So why is this a problem? In a high income, developed economy, by definition wages are high. Because wages are high, however, employers will demand that employees are equipped with the requisite skills—math, language, science, English, computer skills—to perform tasks that create earnings that help offset the high wages. If individuals do not have such skills, employers may take actions to layoff such employees or not hire them in the first place. Employers will look to replace labor with capital and/or move low-skilled jobs off shore. The problem with many countries that have grown fast from poor the middle income and are currently trying to push onto high income status is that there was a disconnect between what students learned in the previous decade or so and what job skills are needed. If a high enough proportion of the labor force is not equipped with the skills needed for a high wage economy, a share of the labor force might become unemployable. As before, if this polarization of the labor force occurs, the only choice of those that are unemployable by the formal labor force would be to move into the informal labor force and/or gray/black economy.
While all economies have such polarized segments of their economy, there are several problems facing middle income countries—especially those that had grown fast in recent years. Dealing with large shares of population in an informal economy requires lots of resources—for unemployment insurance, disability, retraining, health, etc. Since these countries have not yet graduated to high income status, by definition, their level of wealth might make it difficult to spend large sums of money to contain disruption out of the informal economy. If the disruption continues, it can lead to escalating violence and unrest, which will require even more resources to contain. Ironically, the very disruption that is being created by the slowing growth could very well lead to a further slowing of growth if fewer resources are spent on productive investments (instead of containment) and if the disruption itself diminishes interest in investment inside the country. In addition, many of those in the informal economy may exhibit particularly unsatisfied behavior (read anger and disaffection) since the may well feel their original expectations were undermined by the formal establishment. If the size of this part of the population is big enough, the country could find itself atop a powder keg.
In summary, then, the problem with inequality is complicated but real. Inequality in the face of slow growth can lead to unfulfilled expectations and diminished opportunities. Individuals can be polarized into two groups: those inside the system and those outside the system. If inequality is particularly great, the number of those outside the system could be large. Since middle income countries are not rich yet, resources may be insufficient to contain the anger and violence of those in the gray/black economies and/or support the needs of those in the informal economy (who are not contributing a lot to the overall economy). If the disruption is large enough, there could be negative feedback onto growth which could serve to further exacerbate the problem. An end point of stagnation or collapse is certainly plausible.
Our column’s real title: 10 ways to battle inequality; 10 ways to save China’s future
This column is going to be a series of ten articles about China’s inequality. It is a column about how managing that inequality may mean the difference between a bright and vibrant China in 2033 and a China teetering on the edge of collapse. Despite the potential doom, however, this is a column of hope because we believe inequality can be managed—given aggressive, enlightened and motivated decisions TODAY … or at least in the very near future.
However, this column is not about inequality today. We are not going to analyze the accuracy of the estimates of income inequality produced by the China National Bureau of Statistics. We are not going to vote for the higher estimate of Li Shi and his group from Beijing Normal University or the even higher one from Sichuan University’s Li Gan. We are simply going to live with the status quo, one that virtually everyone agrees with: China’s income distribution in 2013 is highly unequal.
Instead we are going to be writing about inequality tomorrow. However, one of the most basic axioms of poverty economics—especially given China’s high inequality today—means that we need to be engaged in this battle against high inequality tomorrow today. The axiom that we are talking about has been made famous both by Nobel Laureates who are spinning their advice for the global economy and by retiring economic planners-cum-policy makers as they write their memoirs. The iron rule of income distribution—lets call this Axiom 1, at some point in the future is:
Tomorrow’s income inequality = Today’s income inequality + Today’s human capital inequality.
This simple formula, above all, embodies on important lesson. Tomorrow’s income inequality is what we are interested in. The first installment of our column today has tried to motivate that this has to be low – or at least not too high – for China to enjoy long-run sustained growth and stable prosperity. We also know—by assumption or by common sense—that Today’s income inequality is high. Hence: to get to where we want to go—that is, low income inequality in the 2030s—we have one and only one degree of freedom. We need to put tremendous attention on reducing human capital inequality today.
If you are following our argument, and if you know anything about the gap between health and education in China today, this column would appear to be one of despair. In fact, this column will fuel that despair. Why? Because are going to show that the human capital gap in China today is ugly. Ugly as in wide. The gap is wide for education. The gap is wide for nutrition. The gap is wide for health. It is wide for babies, preschoolers, elementary school kids, those in middle and high school and for the college-bound. If China does not do anything—and, we mean act seriously—about this gap, and you believe in Axiom 1, it may be time for you to begin to plan for the worst in the coming years.
However, this column will also try to be a source of hope. We will discuss a large number of interventions that work. There are actions that can reduce the human capital gaps at all age levels—from infants to those in elite universities. They are proven. Many are cheap. Many are simple. Some need fundamental rethinking. But, when you add up the price tag of them all and you compare it to the possible costs in the future, we believe a War on Rural Education, Nutrition and Health Inequality is the Best Buy that the government can make.
Stay tuned, then, in the coming months—one column per month. We are going to write about inequality in baby health, nutrition and cognitive abilities between infants in the Qingling Mountains in Southern Shaanxi and China’s tiny princes and princesses in the cities in October. We are going to write about preschool inequality in November. December, January and February will examine the health, nutrition and education crises in poor rural elementary schools and in schools in China’s migrant communities. The rest of the months will talk about inequality in middle school, vocational high school, academic high school and college. There is not a lot of pretty about the gaps that exist in each of these age groups. However, as we stated above, we also will offer solutions—ones that we have evaluated; others that others have initiated. Many of them work. Others need more effort. We will try to inform you of the choices and the hope that can be created by trying. Seriously trying.